In the constantly evolving panorama of health technology, the debate on the smartwatch vs. the precision of medical devices has become a hot topic.
With the ascent of smartwatches in daily life, people turn more and more to these devices for health monitoring. But how do they accumulate against traditional medical devices?
We immerse ourselves in the world of health technology and find out which option offers the most reliable monitoring for your health needs.
Understanding of smartwatches and medical devices
Before being able to compare the accuracy of smartwatches and medical devices, it is essential to understand what everyone does. Smartwatches, such as Apple Watch or Fitbit, are designed for everyday consumers, offering functionality such as heart rate monitoring, step count, sleep monitoring, and even ECG functionality.
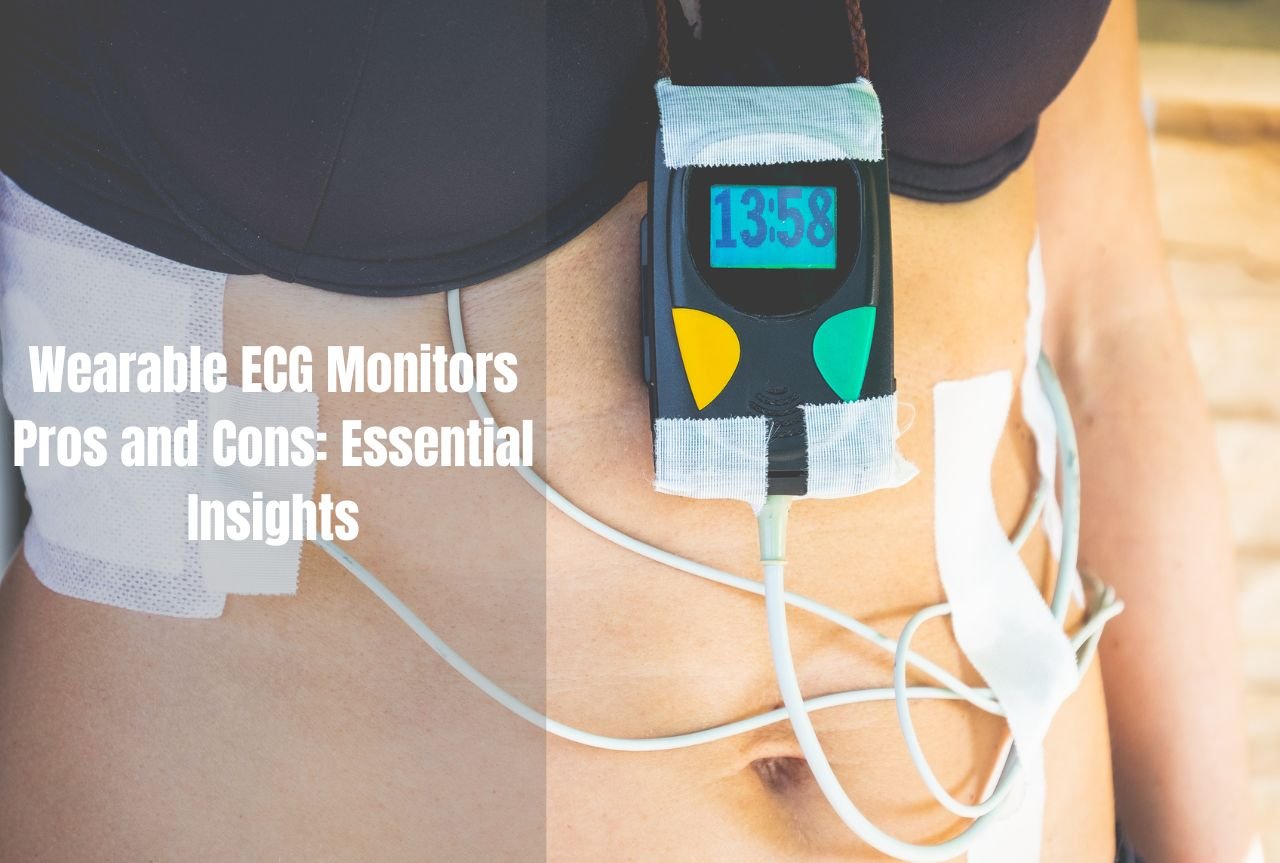
On the other hand, medical devices, such as ECG machines, blood sugar and wrist counters, are specifically designed for clinical accuracy and are often used by healthcare professionals to monitor patients.
As smartwatches measure health metrics
Smartwatches use a variety of sensors to keep track of health metrics. These include:
- Heart rate sensors: Most smartwatches use photoplethysmography (PPG) to measure heart rate. This technology provides that they shines a light through the skin and detects changes in the volume of the blood.
- ACCELEROMETERS: To keep track of passages and movement, smartwatches are based on accelerometers that detect movement in three dimensions.
- Giroscopi: These help measure orientation and can improve fitness monitoring, in particular during activities such as running or cycling.
- GPS: Many smartwatches are equipped with GPS to keep track of the distance and position during outdoor activities.
Medical devices: the Gold Standard
Medical devices are regulated and must meet severe precision standards established by the health authorities. They are generally used in clinical contexts and include devices such as:
- Electrocardiograms (ECGs): These machines provide precise measurements of heart activity by recording electrical signals from the heart.
- Blood pressure monitor: These devices measure blood pressure with high precision and are essential for the diagnosis of hypertension.
- Meters of glucose: Used by diabetics, these devices measure blood sugar levels and are crucial for disease management.
- Pulse Ossimeters: These measure blood oxygen levels and are widely used in hospitals and clinics.
Accommodation comparison: Smartwatch vs medical device
When it comes to comparing the accuracy of smartwatches vs medical devices, several studies have shown that while smartwatches have improved significantly over the years, they still cannot match the precision of dedicated medical equipment.
Heart rate monitoring
The research indicates that smartwatches can trace heart rate with reasonable precision during rest and the activity of light. However, during high-intensity training, discrepancies may arise. Studies show that medical devices, such as ECGs, are more reliable for the diagnosis of arrhythmias and other heart conditions.
Steps count
Smartwatches are quite effective in counting steps, but sometimes they can be off, especially during activities involving the movement of the arm without movement of the legs, such as cycling. Medical devices generally do not measure steps, so this is a unique area in which smartwatches excel.
Blood pressure monitoring and glucose
Smartwatches began to incorporate the monitoring characteristics of blood pressure and glucose, but their precision is often questioned. Clinical devices remain the Gold Standard for these measurements, since they are calibrated and validated for precise readings.
Sleep tracking
When it comes to monitoring sleep models, smartwatches can provide insights based on the movement and variability of the heart rate. However, they may not be as accurate as polysomnography, the clinical standard for studying sleep, which measures brain waves, heart rate, and breathing.
Advantages of smartwatches
Despite the precision gap, smartwatches offer several advantages:
- Accessibility: Smartwatches are widely available and can be used by anyone, providing insights on health without the need for a doctor’s visit.
- Convenience: Users can keep track of their health metrics in real time from their wrists, making it easy to monitor daily activity and fitness objectives.
- Integration: Smartwatches often synchronize with apps that allow users to keep track of their health data over time, providing a complete view of their health path.
Smartwatch limitations
However, smartwatches have some limitations:
- Precision: As mentioned, they may not always provide the most accurate health metrics, especially for serious health conditions.
- Battery life: Frequent use of sensors can quickly drain the battery life, requiring regular charging.
- Data privacy: With so much data on personal health collected, users must be aware of the concerns about privacy and data security.
Make The Right Choice
When it comes to smartwatch precision against medical devices, the right choice depends largely on your health needs. If you are looking for a convenient way to keep track of health metrics and general fitness levels, a smartwatch may be perfect. However, if you are managing a specific health condition or you need precise measurements, traditional medical devices are probably the best solution.
As the technology continues to evolve, the gap between smartwatches and the accuracy of medical devices is shrinking. In the future, we could still see greater integration and progress that allow smartwatches to become more reliable for monitoring critical health.